Facebook is great for getting connected with old friends and maintaining relationships, but it leaves you bare naked on a lot of your privacy wishes, by default. It also exposes both you AND your friends information to 3rd parties that probably should NOT have access to it. YOU can actually leak your own friends private information to third parties, so using a site like Facebook puts a burden of responsibility on you not just for your own privacy and security, but for your friends too.
Here are my recommendations for privacy and security settings on Facebook and explanations of why to set them that way:
Let’s get to your account settings first. Open the “Settings” menu in the upper right corner and choose: “Account Settings”:
Account Settings:
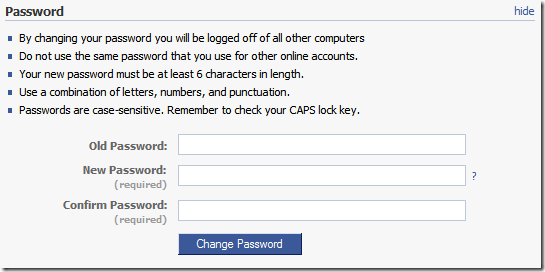
Your password should NOT have a word from the English language in it. There are thousands of hackers out in the wild running software 24/7 trying to hack your account by trying all the words in the English dictionary. I recommend thinking of a sentence that you won’t forget, then entering the first letter of every word. Then, think of a number that’s relevant to that sentence… maybe a date? Put that in there too (at the beginning or end). Between the two, put a special character like “!” or “@” or anything else. If you want, and if you can remember which, make some of your alphabetic characters uppercase and others lowercase.
Here’s an example. Suppose your sentence is: I really like pepperoni pizza. Suppose you had pizza on your first date with your spouse. Pick a date that’s important (the date you met, the date you first had pizza together, the date you got engaged or married). Now, make a password out of it:
“I really like pepperoni pizza” becomes “irlpp”. Suppose the important date was 2/3/1995. Now, pick a special character, say “@”. Now you’ve got a password that you can remember, but no one can crack: “irlpp@1995”.
Remember, if someone hacks your account, not only do they get YOUR private information, but they have access to everything about your friends that YOU DO!!! You’ve got a moral responsibility to protect your friends. Change your password to a rock solid one.
Now, for linked accounts:
I recommend against this. It’s not a good idea to provide a connection path from all of your online accounts. It just makes it easier for hackers who’ve maybe successfully hacked one of your accounts, to then discover what other accounts you have and hack those too.
Privacy Settings:

Choose “Privacy Settings” from the menu above.
By default, I recommend setting everything to “Only Friends”, and escalate to higher publicity only if there’s a really good reason.
- Profile:
- Basic:
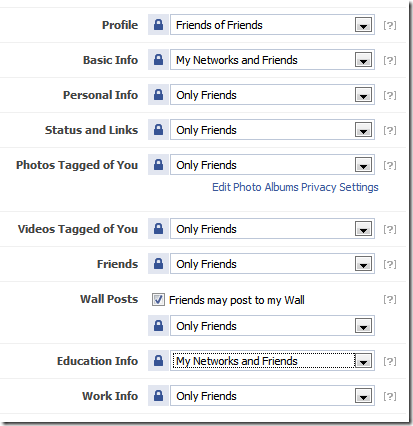
- For Profile, I say go ahead and escalate this up to “Friends of Friends”. It makes it easier for your friends that haven’t connected with you yet (whom the two of you may have mutual friends) to find you, but without exposing yourself to the entire public.
- Basic Info: You can click the little [?] next to it to see what it is. It isn’t much, and I’d say it’s OK for you to escalate this up to your networks. Be careful what networks you join though. Don’t join a network unless there’s a good reason. Every time you join one, you’re increasing your exposure of your personal information.
- Educaton info: Exposing this to networks allows potential friends to identify you by the school you went to, but without completely exposing it to the public.
- Work Info: I’m a strong believer of separating work and private life. You really don’t want all your personal stuff being viewed by the people you work with, especially your supervisors and bosses.
- Keeping your information hidden from the public helps prevent a LOT of uncomfortable situations. Suppose your boss finds you on facebook and wants to friend you? How do you say “no”? If your information isn’t findable, you don’t have to be in that situation.
- Contact Info:

- There’s no reason to expose ANY of this information except to people you’ve already friended. (The last one is my e-mail address, which I’ve erased for obvious reasons).
- Website: If this is a personal web site, you might not want it exposed. If it’s a web site you want public traffic to (say it’s an online store, like www.MichaelsAttic.com (you like how I plugged my own site in this article? :), you may want to make it as public as possible).
Application Settings:
Go back to this menu:

and choose “Application Settings”:

You should check this frequently. I’m constantly finding applications here that I did not grant access to my stuff. Every one that has an “X” beside it (on the right) is one that you can deny access by clicking the “X”. When I grabbed this screen shot, I found “causes” and “vampire wars” showing up here, which I know I did not grant access. They keep showing up and I have no idea why. You’ll have to be vigilant here to continuously delete these applications.
Speaking of Facebook applications, did you know that none of them are actually on Facebook? They’re written by just ordinary Joes, like you and me. As a matter of fact, I have a facebook developer’s license. I can write one too. ANY facebook user can get a developer account and start making applications. You simply CANNOT trust the publishers of these applications to keep your stuff private or to play fair, not even for very popular facebook applications. Don’t believe me? Watch this video of the creator of Mafia Wars and FarmVille (probably the two MOST POPULAR facebook applications):
I don’t play either of those games, but I did sign up for FarmVille because so many of my friends and family have. I’m now going to block it too, and I suggest you do too.
Now, onto your privacy/search options:
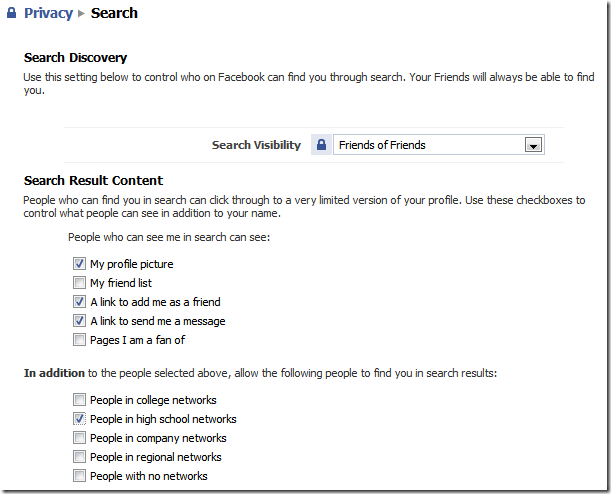
You need to strike a balance between letting your profile be public enough where friends can find you, but private enough so that you’re not totally exposed. For “Search Visibility”, I recommend “Everyone” if you’re just getting started with Facebook, but make sure your “My friend list” is disabled. That’s about the only way your initial set of friends are going to find you. After you’ve got 20 or so friends, I recommend lowering this to “Friends of Friends” and turning back on “My friend list”. Chances are pretty good that most of the rest of your friends will be able to find you through your existing friends.
I recommend against showing pages you’re a fan of to the public. Maybe for friends of friends, at the most. I go by the rule of: “Unless there’s a need for them to have the info, block it”.
Privacy/News Feed and Wall:

I recommend turning off notifications for changes in your relationship status. Unless you really want to broadcast to everyone, “Hey! I just broke up with XXXX!”, it’s probably a good idea to leave it off if you’re currently in a relationship. If you’re not, not much harm in announcing that you just started a relationship (but that’s debatable. You should seriously consider all the people that will see the announcement first).
If you’re removing information from your profile, you’re probably doing it for a reason and advertising to everyone that you’re doing it is probably a bad idea and counter to your reason for removing it, so disable “Remove profile info” so it doesn’t get broadcast.
A lot of people are involved in politics, but have friends on both sides of the aisle. You probably don’t want your posts to political discussion boards broadcast to all of your friends. Best to turn this off.
Advertisements:
Some facebook ads can get your personal info and display it to your friends in the ad. That’s just not right. Set it to “No one”.

When you become a fan of something, it gets broadcast to your friends in the advertisement sections. Unless you want everyone to know you’re a fan of “flipping the pillow to find the cold side”, I recommend setting this to “no one”.
What others can see: I recommend turning all this off except for the select few I have here:


This one’s a REALLY bad idea. Check mark this to prevent it from happening.

Same here. If you’re NOT on facebook, and are participating on some other website, some of them have the ability to post back to your newsfeed what you just did on that other web site. This should be blocked unless you’re fully aware of each and every time it happens.
















